Elevate Your Product Presentation with the Primera LX4000
In today’s competitive market, striking product labels are essential for capturing customer attention. The Primera LX4000 inkjet roll label printer is a fantastic solution for businesses looking to produce high-quality, full-color labels on demand. This compact yet powerful printer brings professional-grade printing capabilities right to your desktop, allowing you to create stunning labels with vibrant colors and sharp details, all without the need for large print runs.
Whether you’re launching a new product, updating branding, or simply need short runs of custom labels, the LX4000 offers incredible flexibility and cost-effectiveness. Its ability to print beautiful, durable labels quickly makes it an invaluable asset for small to medium-sized businesses.
At LaserInkjetLabels.com, we understand the importance of reliable supplies. That’s why we offer a wide variety of Standard Roll Labels specifically designed and tested to perform flawlessly with your Primera LX4000. Our extensive selection includes diverse materials and sizes, ensuring you find the perfect match for your product and application. From glossy and matte papers to durable synthetics, we have the ideal roll labels to bring your designs to life.
Explore our full range of compatible roll labels and find the perfect fit for your LX4000 today: Explore Labels
Foil Stamping on Clear Laser Labels
How to Foil Stamp Using Clear Laser Labels (8.5″ x 11″)
Foil stamping is a simple yet powerful way to enhance the appearance of your printed materials, giving them a premium, eye-catching finish. At LaserInkjetLabels.com, our 8.5″ x 11″ clear laser labels are a popular choice for DIY foil stamping projects—especially among small business owners, crafters, and designers who want to elevate packaging, invitations, or promotional products.

In this guide, we’ll walk you through how to foil stamp using our clear laser labels, including the types of printers that work best, proper printer settings, and key tips to get the best results.
What Is Foil Stamping?
Foil stamping is a process where metallic foil (usually in gold, silver, or holographic finishes) is adhered to printed toner using heat and pressure. When used with clear labels, the effect is especially stunning: the foil appears to float seamlessly on the surface it’s applied to, whether it’s glass, plastic, or product packaging.
Materials You’ll Need
To get started with foil stamping on our 8.5” x 11” clear laser labels, you’ll need the following:
- Clear Gloss Laser Labels (available by the sheet at LaserInkjetLabels.com)
- A monochrome laser printer (see recommended types below)
- Foil transfer sheets (available from craft suppliers in various finishes)
- A laminator or foil applicator machine (capable of reaching high temperatures)
Best Printers for Foil Stamping
For successful foil transfer, it’s essential to use a laser printer that deposits a thick, even layer of toner, as foil adheres only to the toner (not to ink or unprinted areas).
Recommended printer types:
- Monochrome Laser Printers – These are ideal for foil stamping because they apply dense black toner without color mixing. Models by HP, Brother, and Canon are commonly used.
- Color Laser Printers (with caution) – Some color laser printers work well, but results can vary due to differences in toner formulation. If you already own a color laser printer, we recommend testing with our free sample sheets.
Avoid using:
- Inkjet printers (toner is required)
- Low-heat or eco-mode laser printers (insufficient toner melting may occur)
Printer Settings for Best Results
Proper printer setup is crucial to successful foil stamping. Follow these steps:
- Use the correct media setting
Set your printer to “Labels,” “Heavy Paper,” or “Transparency” mode. This increases the fuser temperature and slows down the feed, ensuring better toner adhesion to the clear polyester surface. - Set to monochrome (black only)
Foil transfer only works on black toner. If you’re using a color laser printer, make sure your design is set to print in 100% black. - Print at the highest quality setting
Choose “Best” or “High Resolution” in your printer preferences to maximize toner density. - Let the toner cool
After printing, allow the sheet to cool for 1–2 minutes to prevent smudging during foil application.
How to Apply the Foil
Once your label sheet is printed, it’s time to apply the foil:
- Place the foil
Cut a piece of foil slightly larger than the printed area. Lay it shiny side up over the toner design. - Sandwich the label sheet
Use a protective carrier folder (such as parchment paper or a Teflon sheet) to prevent foil residue from damaging your laminator. - Run through a laminator
Set your laminator to high heat (around 300°F / 150°C) and slow speed. Run the label sheet with foil through the laminator once or twice to ensure good adhesion. - Peel the foil
Allow the sheet to cool, then gently peel away the foil. You should see the metallic foil precisely covering the toner areas on your clear label.
Tips for Best Results
- Always test first: Printer toner and foil results can vary. We strongly recommend ordering a free sample of our clear labels to test your setup.
- Avoid overly fine lines: Thin fonts or intricate designs may not transfer foil cleanly.
- Try different foils: Not all foils are equal—some work better with certain toners or laminator heat settings.
- Laminate for durability: If you’re using the foil-stamped labels outdoors, consider applying a clear laminate for extra protection.
Bring Your Designs to Life
Whether you’re creating luxury product labels, wedding invitations, or custom stickers, foil stamping on our clear laser labels adds a professional, polished look with minimal equipment. With a little practice, you can create standout labels at a fraction of the cost of outsourced foil stamping.
Ready to get started? Browse our clear gloss laser labels and request your free sample sheet today!
5 Reasons to Choose Blank Inkjet Semi-Gloss Labels

If you’re looking for high-quality labels that deliver a professional look, Inkjet Semi-Gloss Labels are the perfect choice. Whether you’re labeling products, packaging, or marketing materials, these labels provide a polished appearance with excellent print quality. Here’s why they stand out:
1. Vibrant, High-Quality Printing
Semi-gloss labels enhance color vibrancy and sharpness, making your designs pop. Whether you’re printing logos, barcodes, or full-color images, these labels ensure crisp, professional results.
2. Sleek, Polished Appearance
With a slight sheen, semi-gloss labels offer a premium look without excessive glare. This makes them perfect for branding, product packaging, and promotional materials that need to stand out.
3. Durable & Smudge-Resistant
Designed for inkjet printers, these labels quickly absorb ink to prevent smudging. Their semi-gloss coating adds durability, making them resistant to handling and minor moisture exposure.
4. Versatile for Various Applications
Ideal for bottles, jars, mailers, boxes, and more, these labels are a go-to choice for businesses and DIY projects alike. Whether you’re labeling handmade goods or shipping products, they provide a professional touch.
5. Easy to Print & Apply
Compatible with most inkjet printers, these labels are user-friendly and hassle-free. Their strong adhesive ensures they stick securely to different surfaces, keeping your labels looking flawless.
Upgrade your branding today! Order your White Semi-Gloss Inkjet labels now!
Roll Label Printing at Home

- Discovering the Creative Side of Roll Label Printers for Personal Projects
Roll Label Printers aren’t just for businesses—they can be used in countless ways to add a personal touch to various projects. From custom gift tags for birthdays and weddings to creating unique home decor with printed patterns, roll label printer’s high-quality prints bring creativity to life. You can even use them for scrapbooking, personalizing jars for a homemade candle business, or labeling family heirlooms with beautiful, decorative fonts. - Innovative Ways to Use Labels Beyond Shipping and Organization
Labels have so much potential beyond traditional uses like shipping and organization. For example, you can use them for custom-designed planner stickers, fun DIY party favors, or as creative bookmarks. You can also design unique labels for your kitchen or pantry, making it a fun way to organize your spices or homemade jams while showcasing your design skills. - Transforming Your Business Image with Customized Labels
Customized labels offer businesses the chance to elevate their brand. Whether you’re creating product packaging, promotional giveaways, or even business cards, personalized labels can help reinforce your brand’s identity. By using distinct color schemes, fonts, and logos, you can create a cohesive, professional image for your company that attracts attention and builds customer trust. - From Labels to Art: Unique DIY Projects with Roll Label Printers
Roll Label Printers can be used as tools for creative DIY projects, allowing individuals to transform their labels into pieces of art. Whether it’s creating intricate label-based collages, printing custom decals for walls, or designing a custom art piece using unique fonts and colors, the possibilities are endless. You can even design labels to use as wall art in a gallery-style setup or turn them into fun, personalized stationery items like greeting cards or notepads.
Each of these topics touches on how Roll Label Printers go beyond their traditional purpose, offering countless ways to add a personal touch to both business and personal projects. You could explore any one of these ideas further, highlighting specific examples or case studies to inspire others! Would you like to dive deeper into any of these?
Roll Label Printing vs Sheet Label Printing
Roll label printing and sheet label printing are two popular methods used for creating labels. Both methods have their own advantages and disadvantages, making them suitable for different applications. Roll label printing involves printing labels on a continuous roll of material, which can be cut into individual labels as needed. This method is ideal for large volume production runs, as it allows for efficient printing and cutting of large quantities of labels
.
Additionally, roll labels tend to be more durable than sheet labels, making them suitable for labeling products that may be exposed to harsh conditions. Sheet label printing involves printing individual labels on a sheet of material that is then cut into separate labels. This method is ideal for smaller production runs or when multiple designs are needed on the same sheet.
Sheet labels are also often used in office settings for labeling files, folders, and other documents.
Roll label printing and sheet label printing are two of the most commonly used methods for producing labels. While both methods result in high-quality labels, there are some key differences between the two. Roll label printing involves printing labels on a continuous roll of material. This method is ideal for large-scale production runs, as it allows for faster printing speeds and reduced set-up time.
Roll labels are also easier to apply with automated labeling machines, making them popular in industries such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and logistics. Sheet label printing involves printing individual labels on pre-cut sheets of material. This method is ideal for smaller production runs or custom jobs that require variable data or designs. Sheet labels can be easily handled and stored, making them popular in office environments or for small businesses.
Ultimately, the choice between roll label printing and sheet label printing will depend on factors such as the quantity of labels needed, the complexity of the design, and the intended application.
Roll label printing offers several advantages. Firstly, it is a more efficient method for large-scale printing, as it allows for faster print speeds and reduced downtime between jobs. Secondly, roll labels are easier to apply to products, as they can be easily dispensed using a label applicator or dispenser. Finally, roll labels take up less storage space and are easier to transport than sheet labels.
However, there are also some disadvantages to roll label printing. One of the main drawbacks is that it requires specialized equipment and machinery to print and apply the labels. Additionally, roll labels can be more expensive per unit than sheet labels for smaller print runs. On the other hand, sheet label printing has its own set of advantages. It is more cost-effective for smaller print runs and does not require specialized equipment or machinery.
Printing Custom Label Shapes
Create Custom Shaped Labels on Rolls
Our roll labels offer the ability to effortlessly print custom label shapes. With this innovative solution, you can forgo the usual setup and registration hassles involved in printing odd shaped labels. Our custom roll label shapes have been specifically designed to streamline the process of aligning your artwork. Gone are the days of worrying about the printer’s optical eye registration missing or misinterpreting the label spacing. With our method, each shape will be consistently printed exactly where you need it.
The beauty of our approach lies in its simplicity. We enclose your chosen shape inside a rectangle, as depicted in the accompanying image. For instance, if you opt for a heart-shaped label, our technique ensures that your printer will unfailingly recognize the label gap, allowing for precision printing. Have several smaller labels? We can several label sizes into a rectangle so you can print several in one pass. Moreover, our method offers the added benefit of extending the color beyond the edge of the custom-shaped label. This feature enables the color to bleed off the label without any concerns about ink spreading to the liner, rollers, or the next label, which could otherwise compromise the image quality.
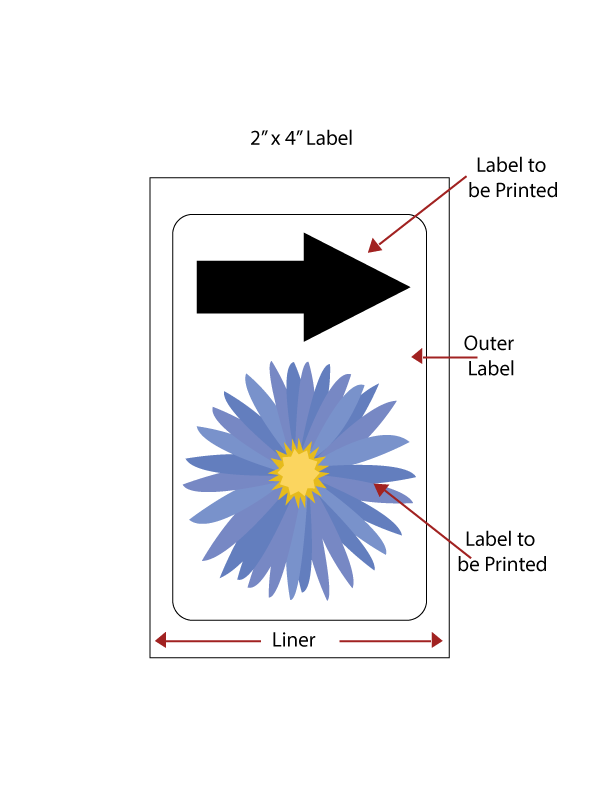
LaserInkjetLabels.com can create any shape you need to print. Call now or email us for a quote.
Matte vs Glossy Labels
Labels play an essential role in product packaging as they convey important information about the product and its contents. The choice of label finish can significantly impact the overall look and feel of the package. Matte and glossy labels are two popular options for labeling products, each with their unique characteristics. Matte labels have a flat, non-reflective finish that gives them a more understated and subtle appearance.
They are ideal for products that require a more natural or rustic look, such as organic food or handmade goods. On the other hand, glossy labels have a shiny, reflective finish that enhances the colors and graphics on the label, making them stand out more prominently. They are often used for products that require a sleek and professional appearance, such as electronics or cosmetics.
Ultimately, selecting between matte and glossy labels depends on the product’s branding needs and design goals to create an eye-catching package that appeals to customers.
When it comes to choosing between matte and glossy labels, there are several factors to consider. Matte labels have a non-shiny finish that makes them ideal for product labeling. They are also more durable and resistant to smudging, making them suitable for products that will be handled frequently. In addition, matte labels are great for printing small text and barcodes as they provide better contrast.
On the other hand, glossy labels have a shiny finish that gives them a more professional look. They are perfect for high-end products and promotional materials because they catch the light and draw attention. Glossy labels also have a protective layer that makes them more resistant to water damage. However, glossy labels can be difficult to read in direct sunlight due to their reflective surface.
They are also prone to smudging and fingerprints, which can make them less appealing over time. Ultimately, the decision between matte vs glossy labels depends on your specific needs and preferences.
How to determine which software program to use to make your labels.
When it comes to label making, choosing the right software can make all the difference. With so many options available, it can be overwhelming to determine which program is best suited for your needs. Here are some key factors to consider when selecting label making software:
- Compatibility: Make sure the software is compatible with your operating system and printer.
- Features: Look for software that offers the features you need, such as barcode generation, graphic design tools, and database integration.
- Ease of use: Choose software that is user-friendly and easy to navigate, especially if you are new to label making.
- Support: Consider software that offers technical support and tutorials to help you troubleshoot any issues that may arise.
By taking these factors into account, you can choose the right software program to create professional-looking labels that meet your specific needs.
Commercial Label Printing
Commercial printing refers to the process of printing high-quality materials for businesses, organizations, and individuals. It involves producing large quantities of printed materials such as brochures, business cards, flyers, posters, label materials, and banners using advanced printing equipment. Commercial printers utilize various printing techniques such as digital, offset, and letterpress to create visually appealing and engaging printed products. With the advent of digital technology, commercial printing has evolved significantly over the years offering faster turnaround times and cost-effective solutions to meet the unique needs of clients.
This subtopic will explore the world of commercial printing in detail.
The beginnings of commercial printing can be traced back to the 15th century with the invention of the printing press by Johannes Gutenberg. Prior to this, books were hand-copied by scribes and were expensive and time-consuming to produce. Gutenberg’s press revolutionized the industry by allowing for mass production of printed materials, making them more affordable and accessible to a wider audience.
The first commercial printers focused on producing religious texts, but as demand grew, they expanded into other areas such as newspapers, pamphlets, and eventually advertising materials. This marked the beginning of modern commercial printing.
Advancements in printing technology have revolutionized the commercial printing industry, making it faster, more efficient and cost-effective. The introduction of digital printing has allowed for on-demand and variable data printing, enabling businesses to print smaller quantities with personalized content at a lower cost. The use of UV and LED curing technologies have also improved the quality and durability of printed materials while reducing drying time.
Modern commercial printing techniques have revolutionized the way businesses print their marketing materials. Digital printing is now the most popular technique, which uses inkjet or laser printers to produce high-quality prints with excellent color accuracy. This method is ideal for short runs and variable data printing, such as personalized direct mail campaigns. Offset printing still has its place in long-run projects that require precise color matching and consistent quality.
Commercial label printing offers numerous benefits to businesses, including cost-effectiveness, high-quality printing, and customization options. By outsourcing printing needs to a professional printer, businesses can save money on equipment and supplies while ensuring that their marketing materials are produced with the highest quality standards. Additionally, commercial printers can offer customization options such as variable data printing, which allows for personalized marketing campaigns.
Finally, commercial printers often have quick turnaround times and can handle large volume orders efficiently, allowing businesses to focus on other aspects of their operations.
The future of commercial printing is exciting, with several trends and innovations emerging. One of the most significant changes is the shift towards digital printing, which offers greater flexibility and faster turnaround times. Automation and artificial intelligence are also transforming the industry, making it easier to manage complex print jobs with fewer errors. Personalization and customization are becoming increasingly important, with companies offering tailored solutions for individual clients.
Finally, eco-friendly practices such as using sustainable materials and reducing waste are gaining traction in the industry as customers become more environmentally conscious.
Check out our Custom Label Printing Section here
Information On Primera Roll Label Printers
Primera Technology is a leading manufacturer of specialized digital printing equipment, including roll label printers. These printers are designed to produce high-quality labels for a variety of industries, including food and beverage, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and more. Primera roll label printers offer exceptional print quality with vibrant colors and sharp text. They are ideal for printing small to medium-sized batches of labels quickly and efficiently.
With easy-to-use software and intuitive controls, Primera roll label printers are an excellent choice for businesses looking to streamline their label printing process. In this article, we will explore the features and benefits of Primera roll label printers in more detail. We will also provide information on the different models available and how they can help your business improve its labeling capabilities.
The features and benefits of Primera roll label printers are numerous and varied, making them a top choice for businesses of all sizes. One of the key advantages is their high-quality printing, with vibrant colors and sharp text that is easy to read. These printers are also highly versatile, with the ability to print on a wide range of materials including paper, synthetic labels, and even polyester.
Another major benefit is their speed – Primera roll label printers can produce up to 8 inches per second, allowing for quick turnaround times even for large jobs. Additionally, these printers are user-friendly and easy to operate, with intuitive software that simplifies the printing process. Finally, Primera roll label printers offer excellent value for money, with low operating costs and minimal maintenance requirements over time.
When choosing the right Primera roll label printer for your business, there are several factors to consider. Firstly, you need to determine the volume of labels you will be printing and the size of the labels required. This will help you choose a printer that can handle your workload and produce the desired label size. Secondly, consider the type of materials you will be printing on.
If you need to print on specialty materials such as glossy or matte finishes, then choose a printer that can handle these types of media. Thirdly, look at the connectivity options available. If you need to print from multiple devices or over a network, then choose a printer with Wi-Fi or Ethernet connectivity. Finally, consider any additional features such as built-in cutters or color capabilities that may be important for your business needs.
Primera roll label printers are reliable and durable machines that require minimal maintenance. However, regular cleaning and upkeep can extend the life of your printer and ensure it continues to produce high-quality labels. To keep your Primera roll label printer in optimal condition, it is important to regularly clean the print head, platen roller, and label sensor. Primera offers cleaning kits specifically designed for their printers to make this process easy and efficient.
In addition to maintenance, Primera also offers excellent customer support for their printers. Their technical support team is available via phone or email to answer any questions or troubleshoot any issues you may encounter with your printer. For added peace of mind, Primera also offers extended warranty options for their printers.

